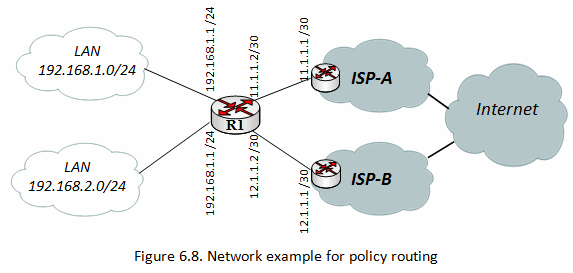
Policy routing implementation example
Install Nagios3.5 on ubuntu14.4 LTS
A. Install
Apache2
Install Apache2 to Configure HTTP Server. HTTP uses 80/TCP.
[1] Install Apache2.
[2] Configure Apache2.
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf
# line 26: change
ServerSignature Off
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dir.conf
# line 2: add file name that it can access only with
directory's name
DirectoryIndex index.html index.htm
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
# line 70: add server name
ServerName www.srv.world
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
# line 11: change admin email address
ServerAdmin webmaster@srv.world
root@www:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting web
server apache2
...done.
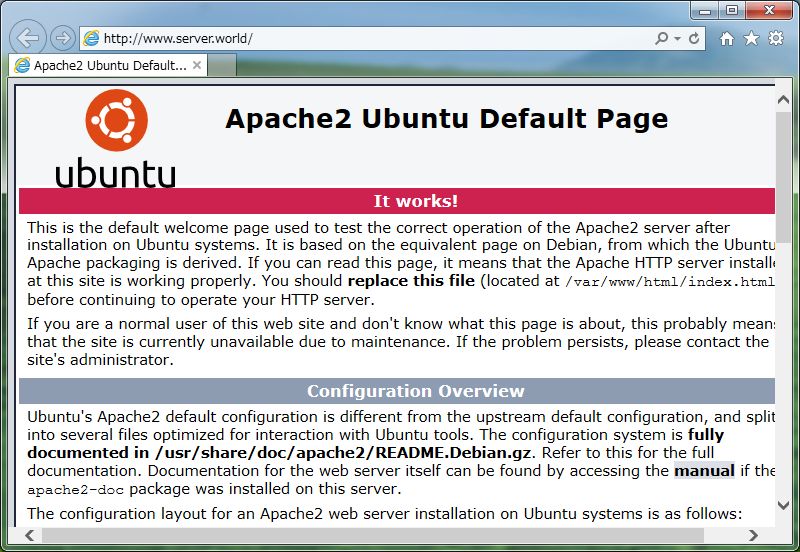
[3] Access to "http://(your server's hostname or IP
address)/" with web browser. It's OK if following page is shown. (default
page)
B.
Use PHP Scripts
Configure Apache2 to use PHP scripts.
[1] Install PHP.
root@www:~# apt-get
-y install php5 php5-cgi libapache2-mod-php5 php5-common php-pear
[2] Configure Apache2.
root@www:~# a2enconf php5-cgi.conf
Enabling conf php5-cgi.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
service apache2
reload
root@www:~# vi /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini
# line 879: uncomment and add
your timezone
date.timezone =
"Asia/Tokyo"
root@www:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting
web server apache2
...done.
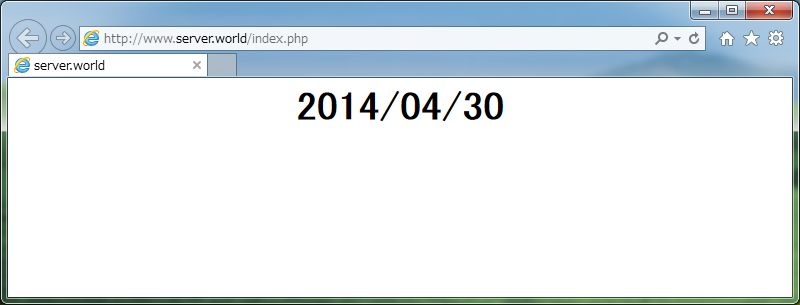
[3] Create a PHP test
page and access to it from any clients with web browser. It's OK if following
page is shown.
root@www:~# vi /var/www/html/index.php
<html>
<body>
<div style="width: 100%;
font-size: 40px; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;">
<?php
print Date("Y/m/d");
?>
</div>
</body>
</html>
C.
Nagios : Install
Install Nagios which is an enterprise open source monitoring system.
[1]Install and start Apache httpd, refer to here.
[1]Install and start Apache httpd, refer to here.
[2]Install PHP, refer to here.
[3] Install Nagios.
Also Install basic plugins to monitor nagios server itself.
root@dlp:~# apt-get -y install nagios3 nagios-plugins-basic
[4] Configure Nagios.
root@dlp:~# vi /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
# line 145: change
check_external_commands=1
root@dlp:~# vi /etc/nagios3/apache2.conf
# line 37: change access permission
Allow From localhost 10.0.0.0/24
# change admin password
root@dlp:~# htpasswd /etc/nagios3/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
New password: #
set password
Re-type new password:
Updating password for
user nagiosadmin
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/nagios3 restart
* Restarting nagios3
monitoring daemon nagios3
...done.
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting web
server apache2
...done.
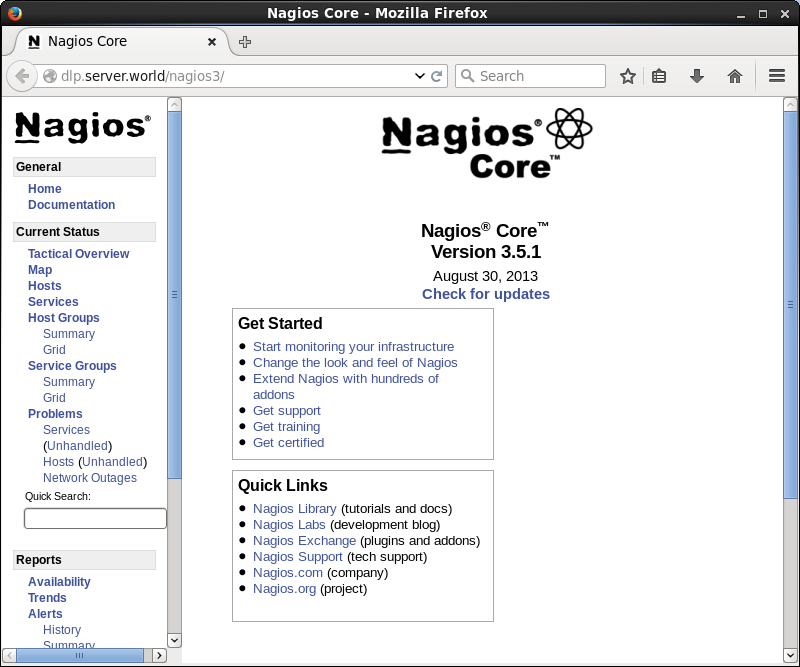
[5] Access to the
"http://(Nagios server's hostname or IP address)/nagios3/" from a
client which is in the network allowed by Nagios server and authenticate with
the Nagios admin user "nagiosadmin" to login.
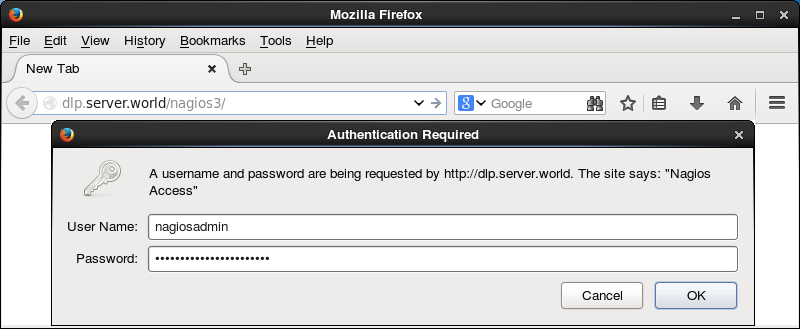
[6] After successing
authentication, the Nagios admin site is displayed.
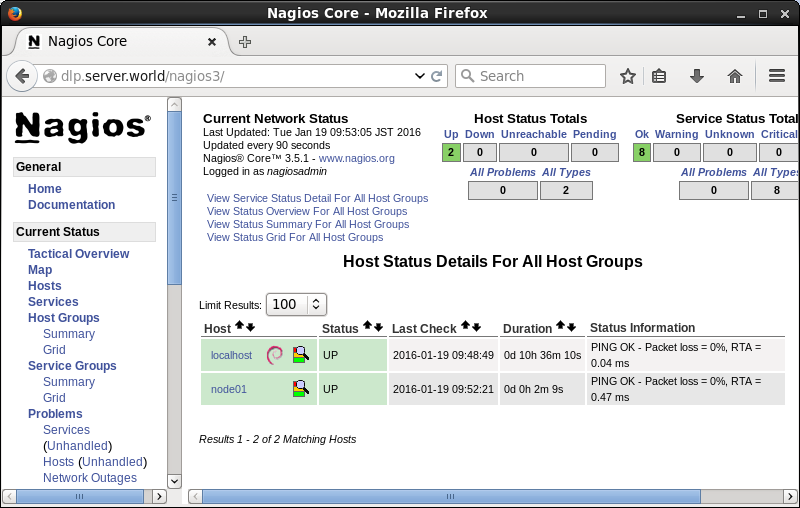
Nagios : Add Monitoring Target
Host#1
It's possible to monitor other servers on the network.
[1] For exmaple, add a
server for monitoring target with simply Ping command.
root@dlp:~# vi
/etc/nagios3/conf.d/node01.cfg
# create new
define host{
use generic-host
host_name node01
alias node01
address 10.0.0.51
}
use generic-service
host_name node01
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
}
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/nagios3 restart
[2] It's possible to view
the status for a new server on the admin site.

Policy base Routing (2 WAN- 2LAN) in mikrotik router
Policy Based Routing (2 WAN- 2LAN) in mikrotik router
We will assume that you already have the IP addresses set up on your router.
First, we must define our routes. We will add three “default” routes. These are below:
/ip route
add gateway=10.10.11.1 routing-mark=ISP2
add gateway=10.10.10.1 routing-mark=ISP1
add gateway=10.10.10.1
add gateway=10.10.11.1 routing-mark=ISP2
add gateway=10.10.10.1 routing-mark=ISP1
add gateway=10.10.10.1
add gateway=10.10.11.1 distance 10
All traffic from the 192.168.0.0/24 network will use ISP1 and all traffic from the 192.168.1.0/24 network will use ISP2. Here is the implementation:
/ip firewall mangle
add chain=prerouting src-address=192.168.0.0/24 dst-address=192.168.0.1 action=accept
add chain=prerouting src-address=192.168.1.0/24 dst-address=192.168.1.1 action=accept
add chain=prerouting src-address=192.168.0.0/24 action=mark-routing \
new-routing-mark=ISP1 passthrough=no
new-routing-mark=ISP1 passthrough=no
new-routing-mark=ISP2 passthrough=no
/ip firewall nat
add chain=src-nat outinterface=ISP1_WAN action=masqurate
add chain=src-nat outinterface=ISP2_WAN action=masqurate
add chain=src-nat WAN action=masqurate
[Ref:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m6tYANGC9o0]
[Ref:http://blog.butchevans.com/2008/09/mikrotik-policy-routing-implementation-example/]SNMP in Cisco Router or Switch
SNMP in Cisco Router or Switch
Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#
Router(config)#snmp-server community public RO ; read onlyRouter(config)#snmp-server community private RW ; read and Write only
Configuring PPTP (VPDN) Server On A Cisco Router
Configuring PPTP (VPDN) Server On A Cisco Router
If you need to allow VPN access to your network from the outside world then setting your Cisco router up to be a PPTP server is an easy way to do it.
Firstly we need to enable VPDN:
vpdn enable ! vpdn-group 1 accept-dialin protocol pptp virtual template 254
Now we need to create the virtual template:
interface virtual-template 254 ip unnumbered fastethernet 0/0 peer default ip address pool pptp-pool no keepalive ppp encrypt mppe auto ppp authentication ms-chap ms-chapv2
Once the Virtual template has been configured we need to create the IP address pool that will be assigned to the PPTP client:
ip local pool pptp-pool 192.168.0.50 192.168.0.60
We will now need to create the username and password that will allow the PPTP client to authenticate with the router:
username pptpuser password pptppassword
Finally we need to allow PPTP through any access-lists we may have on the incoming interface by appending the configuration below:
access-list 123 permit tcp any host 94.142.65.249 eq 1723 access-list 123 permit gre any any
IP sla In Cisco router
Configuring a Basic ICMP Echo Operation
Router cisco 1800
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip sla operation-number
4. icmp-echo {destination-ip-address | destination-hostname} [source-ip {ip-address | hostname} |source-interface interface-name]
5. frequency seconds
6. end
Example
ip sla 10
icmp-echo 192.168.1.1 source-interface GigabitEthernet0/5
threshold 100
timeout 1000
frequency 3
ip sla schedule 10 life forever start-time now
ip sla 20
icmp-echo 192.168.2.1 source-interface GigabitEthernet0/4
threshold 100
timeout 1000
frequency 3
ip sla schedule 20 life forever start-time now
track 10 ip sla 10 reachability
delay down 1 up 1
!
track 20 ip sla 20 reachability
delay down 1 up 1
ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 name PRI track 10
ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1 2 name RDN track 20
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Router cisco 3800
SUMMARY STEPS1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip sla monitor operation-number
4. type echo protocol ipIcmpEcho {destination-ip-address | destination-hostname} [source-ipaddr {ip-address | hostname} | source-interface interface-name]
5. frequency seconds
6. exit
7. ip sla monitor schedule operation-number [life {forever | seconds}] [start-time {hh:mm[:ss] [month day | day month] | pending | now | after hh:mm:ss] [ageout seconds] [recurring]
8. exit
9. track object-number rtr operation-number { state| reachability }
Example
The following example shows the configuration of the IP SLAs ICMP Echo operation number 6 that will start immediately and run indefinitely.
ip sla monitor 10
type echo protocol ipIcmpEcho 172.29.139.134 source-ipaddr 172.29.139.132
threshold 100
timeout 1000
frequency 3
!
ip sla monitor schedule 6 life forever start-time now
track 10 rtr 10 reachability
delay down 1 up 1
ip sla monitor 20
type echo protocol ipIcmpEcho 172.29.139.134 source-ipaddr 172.29.139.1
threshold 100
timeout 1000
frequency 3
!
ip sla monitor schedule 6 life forever start-time now
track 20 rtr 20 reachability
delay down 1 up 1
Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol) and IPSec are essential to building and encrypting the VPN tunnel. ISAKMP , also called IKE (Internet Key Exchange), is the negotiation protocol that allows two hosts to agree on how to build an IPsec security association. ISAKMP negotiation consists of two phases: Phase 1 and Phase 2.
Phase 1 creates the first tunnel, which protects later ISAKMP negotiation messages.
Phase 2 creates the tunnel that protects data. IPSec then comes into play to encrypt the data using encryption algorithms and provides authentication, encryption and anti-replay services.
IPSec VPN Requirements
To help make this an easy-to-follow exercise, we have split it into two steps that are required to get the Site-to-Site IPSec VPN Tunnel to work.
These steps are:
(1) Configure ISAKMP (ISAKMP Phase 1)
3/5/2017 Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
http://www .firewall.cx/cisco-technical-knowledgebase/cisco-routers/867-cisco-router-site-to-site-ipsec-vpn.html 2/6
(2) Configure IPSec (ISAKMP Phase 2, ACLs, Crypto MAP)
Our example setup is between two branches of a small company, these are Site 1 and Site 2. Both the branch routers connect to the Internet and have a static IP Address assigned by their ISP as shown on the diagram:
Site 1 is configured with an internal network of 10.10.10.0/24, while Site 2 is configured with network 20.20.20.0/24. The goal is to securely connect both LAN networks and allow full communication between them, without any restrictions.
Configure ISAKMP (IKE) - (ISAKMP Phase 1)
IKE exists only to establish SAs (Security Association) for IPsec. Before it can do this, IKE must negotiate an SA (an ISAKMP SA) relationship with the peer.
To begin, we’ll start working on the Site 1 router (R1).
First step is to configure an ISAKMP Phase 1 policy:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R1(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R1(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R1(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R1(config-isakmp)# group 2
R1(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
The above commands define the following (in listed order):
3DES - The encryption method to be used for Phase 1. MD5 - The hashing algorithm Pre-share - Use Pre-shared key as the authentication method Group 2 - Diffie-Hellman group to be used 86400 – Session key lifetime. Expressed in either kilobytes (after x-amount of traffic, change the key)
seconds. Value set is the default value. We should note that ISAKMP Phase 1 policy is defined globally. This means that if we have five different remote sites and configured five different ISAKMP Phase 1 policies (one for each remote router), when our router tries to negotiate a VPN tunnel with each site it will send all five policies and use the first match that is accepted by both ends.
Next we are going to define a pre shared key for authentication with our peer (R2 router) by using the following command:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.2
The peer’s pre shared key is set to firewallcx and its public IP Address is 1.1.1.2. Every time R1 tries to establish a VPN tunnel with R2 (1.1.1.2), this pre shared key will be used.
Configure IPSec
To configure IPSec we need to setup the following in order:
- Create extended ACL
- Create IPSec Transform
- Create Crypto Map
- Apply crypto map to the public interface
Let us examine each of the above steps.
Creating Extended ACL
Next step is to create an access-list and define the traffic we would like the router to pass through the VPN tunnel. In this example, it would be traffic from one network to the other, 10.10.10.0/24 to 20.20.20.0/24. Access-lists that define VPN traffic are sometimes called crypto access-list or interesting traffic access-list.
R1(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
Create IPSec Transform (ISAKMP Phase 2 policy)
Next step is to create the transform set used to protect our data. We’ve named this TS:
R1(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
The above command defines the following:
- ESP-3DES - Encryption method - MD5 - Hashing algorithm
Create Crypto Map
The Crypto map is the last step of our setup and connects the previously defined ISAKMP and IPSec configuration together:
R1(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R1(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.2
R1(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R1(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
We’ve named our crypto map CMAP . The ipsec-isakmp tag tells the router that this crypto map is an IPsec crypto map. Although there is only one peer declared in this crypto map (1.1.1.2), it is possible to have multiple peers within a given crypto map.
Apply Crypto Map to the Public Interface
The final step is to apply the crypto map to the outgoing interface of the router. Here, the outgoing interface is FastEthernet 0/1.
R1(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R1(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Note that you can assign only one crypto map to an interface.
As soon as we apply crypto map on the interface, we receive a message from the router that confirms isakmp is on: “ISAKMP is ON”.
At this point, we have completed the IPSec VPN configuration on the Site 1 router.
We now move to the Site 2 router to complete the VPN configuration. The settings for Router 2 are identical, with the only difference being the peer IP Addresses and access lists:
R2(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R2(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R2(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R2(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R2(config-isakmp)# group 2
R2(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.1
R2(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
R2(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R2(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.1
R2(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R2(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R2(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Network Address Translation (NAT) and IPSec VPN Tunnels
Network Address Translation (NAT) is most likely to be configured to provide Internet access to internal hosts. When configuring a Site-to-Site VPN tunnel, it is imperative to instruct the router not to perform NAT (deny NAT) on packets destined to the remote VPN network(s).
This is easily done by inserting a deny statement at the beginning of the NAT access lists as shown below:
For Site 1’s router:
R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 100 interface fastethernet0/1 overload
R1(config)# access-list 100 remark -=[Define NAT Service]=
R1(config)# access-list 100 deny ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# access-list 100 permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 any
R1(config)# access-list 100 remark
And Site 2’s router:
R2(config)# ip nat inside source list 100 interface fastethernet0/1 overload
R2(config)# access-list 100 remark -=[Define NAT Service]=
R2(config)# access-list 100 deny ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)# access-list 100 permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 any
R2(config)# access-list 100 remark
Bringing Up and Verifying the VPN Tunnel
At this point, we’ve completed our configuration and the VPN Tunnel is ready to be brought up. To initiate the VPN Tunnel, we need to force one packet to traverse the VPN and this can be achieved by pinging from one router to another:
R1# ping 20.20.20.1 source fastethernet0/0
Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 20.20.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.10.1 .!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 44/47/48 ms The first ping received a timeout, but the rest received a reply, as expected. The time required to bring up the VPN Tunnel is sometimes slightly more than 2 seconds, causing the first ping to timeout.
To verify the VPN Tunnel, use the show crypto session command:
R1# show crypto session Crypto session current status Interface: FastEthernet0/1
Session status: UP-ACTIVE Peer: 1.1.1.2 port 500 IKE SA: local 1.1.1.1/500 remote 1.1.1.2/500 Active IPSEC FLOW: permit ip 10.10.10.0/255.255.255.0 20.20.20.0/255.255.255.0
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol) and IPSec are essential to building and encrypting the VPN tunnel. ISAKMP , also called IKE (Internet Key Exchange), is the negotiation protocol that allows two hosts to agree on how to build an IPsec security association. ISAKMP negotiation consists of two phases: Phase 1 and Phase 2.
Phase 1 creates the first tunnel, which protects later ISAKMP negotiation messages.
Phase 2 creates the tunnel that protects data. IPSec then comes into play to encrypt the data using encryption algorithms and provides authentication, encryption and anti-replay services.
IPSec VPN Requirements
To help make this an easy-to-follow exercise, we have split it into two steps that are required to get the Site-to-Site IPSec VPN Tunnel to work.
These steps are:
(1) Configure ISAKMP (ISAKMP Phase 1)
3/5/2017 Configuring Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routers
http://www .firewall.cx/cisco-technical-knowledgebase/cisco-routers/867-cisco-router-site-to-site-ipsec-vpn.html 2/6
(2) Configure IPSec (ISAKMP Phase 2, ACLs, Crypto MAP)
Our example setup is between two branches of a small company, these are Site 1 and Site 2. Both the branch routers connect to the Internet and have a static IP Address assigned by their ISP as shown on the diagram:
Site 1 is configured with an internal network of 10.10.10.0/24, while Site 2 is configured with network 20.20.20.0/24. The goal is to securely connect both LAN networks and allow full communication between them, without any restrictions.
Configure ISAKMP (IKE) - (ISAKMP Phase 1)
IKE exists only to establish SAs (Security Association) for IPsec. Before it can do this, IKE must negotiate an SA (an ISAKMP SA) relationship with the peer.
To begin, we’ll start working on the Site 1 router (R1).
First step is to configure an ISAKMP Phase 1 policy:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R1(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R1(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R1(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R1(config-isakmp)# group 2
R1(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
The above commands define the following (in listed order):
3DES - The encryption method to be used for Phase 1. MD5 - The hashing algorithm Pre-share - Use Pre-shared key as the authentication method Group 2 - Diffie-Hellman group to be used 86400 – Session key lifetime. Expressed in either kilobytes (after x-amount of traffic, change the key)
seconds. Value set is the default value. We should note that ISAKMP Phase 1 policy is defined globally. This means that if we have five different remote sites and configured five different ISAKMP Phase 1 policies (one for each remote router), when our router tries to negotiate a VPN tunnel with each site it will send all five policies and use the first match that is accepted by both ends.
Next we are going to define a pre shared key for authentication with our peer (R2 router) by using the following command:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.2
The peer’s pre shared key is set to firewallcx and its public IP Address is 1.1.1.2. Every time R1 tries to establish a VPN tunnel with R2 (1.1.1.2), this pre shared key will be used.
Configure IPSec
To configure IPSec we need to setup the following in order:
- Create extended ACL
- Create IPSec Transform
- Create Crypto Map
- Apply crypto map to the public interface
Let us examine each of the above steps.
Creating Extended ACL
Next step is to create an access-list and define the traffic we would like the router to pass through the VPN tunnel. In this example, it would be traffic from one network to the other, 10.10.10.0/24 to 20.20.20.0/24. Access-lists that define VPN traffic are sometimes called crypto access-list or interesting traffic access-list.
R1(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
Create IPSec Transform (ISAKMP Phase 2 policy)
Next step is to create the transform set used to protect our data. We’ve named this TS:
R1(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
The above command defines the following:
- ESP-3DES - Encryption method - MD5 - Hashing algorithm
Create Crypto Map
The Crypto map is the last step of our setup and connects the previously defined ISAKMP and IPSec configuration together:
R1(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R1(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.2
R1(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R1(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
We’ve named our crypto map CMAP . The ipsec-isakmp tag tells the router that this crypto map is an IPsec crypto map. Although there is only one peer declared in this crypto map (1.1.1.2), it is possible to have multiple peers within a given crypto map.
Apply Crypto Map to the Public Interface
The final step is to apply the crypto map to the outgoing interface of the router. Here, the outgoing interface is FastEthernet 0/1.
R1(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R1(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Note that you can assign only one crypto map to an interface.
As soon as we apply crypto map on the interface, we receive a message from the router that confirms isakmp is on: “ISAKMP is ON”.
At this point, we have completed the IPSec VPN configuration on the Site 1 router.
We now move to the Site 2 router to complete the VPN configuration. The settings for Router 2 are identical, with the only difference being the peer IP Addresses and access lists:
R2(config)# crypto isakmp policy 1
R2(config-isakmp)# encr 3des
R2(config-isakmp)# hash md5
R2(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
R2(config-isakmp)# group 2
R2(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key firewallcx address 1.1.1.1
R2(config)# ip access-list extended VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
R2(config)# crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
R2(config-crypto-map)# set peer 1.1.1.1
R2(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set TS
R2(config-crypto-map)# match address VPN-TRAFFIC
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1
R2(config- if)# crypto map CMAP
Network Address Translation (NAT) and IPSec VPN Tunnels
Network Address Translation (NAT) is most likely to be configured to provide Internet access to internal hosts. When configuring a Site-to-Site VPN tunnel, it is imperative to instruct the router not to perform NAT (deny NAT) on packets destined to the remote VPN network(s).
This is easily done by inserting a deny statement at the beginning of the NAT access lists as shown below:
For Site 1’s router:
R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 100 interface fastethernet0/1 overload
R1(config)# access-list 100 remark -=[Define NAT Service]=
R1(config)# access-list 100 deny ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# access-list 100 permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 any
R1(config)# access-list 100 remark
And Site 2’s router:
R2(config)# ip nat inside source list 100 interface fastethernet0/1 overload
R2(config)# access-list 100 remark -=[Define NAT Service]=
R2(config)# access-list 100 deny ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)# access-list 100 permit ip 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 any
R2(config)# access-list 100 remark
Bringing Up and Verifying the VPN Tunnel
At this point, we’ve completed our configuration and the VPN Tunnel is ready to be brought up. To initiate the VPN Tunnel, we need to force one packet to traverse the VPN and this can be achieved by pinging from one router to another:
R1# ping 20.20.20.1 source fastethernet0/0
Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 20.20.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.10.1 .!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 44/47/48 ms The first ping received a timeout, but the rest received a reply, as expected. The time required to bring up the VPN Tunnel is sometimes slightly more than 2 seconds, causing the first ping to timeout.
To verify the VPN Tunnel, use the show crypto session command:
R1# show crypto session Crypto session current status Interface: FastEthernet0/1
Session status: UP-ACTIVE Peer: 1.1.1.2 port 500 IKE SA: local 1.1.1.1/500 remote 1.1.1.2/500 Active IPSEC FLOW: permit ip 10.10.10.0/255.255.255.0 20.20.20.0/255.255.255.0
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)