A. Install
Apache2
Install Apache2 to Configure HTTP Server. HTTP uses 80/TCP.
[1] Install Apache2.
[2] Configure Apache2.
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf
# line 26: change
ServerSignature Off
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dir.conf
# line 2: add file name that it can access only with
directory's name
DirectoryIndex index.html index.htm
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
# line 70: add server name
ServerName www.srv.world
root@www:~# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
# line 11: change admin email address
ServerAdmin webmaster@srv.world
root@www:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting web
server apache2
...done.
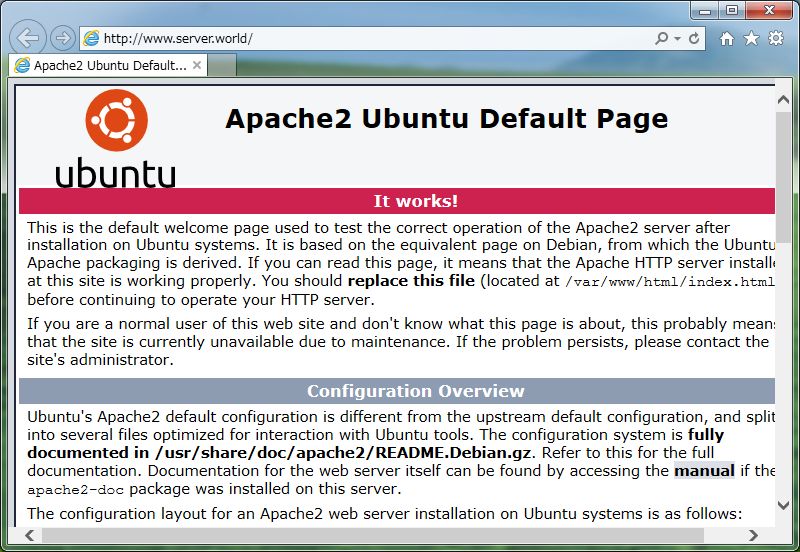
[3] Access to "http://(your server's hostname or IP
address)/" with web browser. It's OK if following page is shown. (default
page)
B.
Use PHP Scripts
Configure Apache2 to use PHP scripts.
[1] Install PHP.
root@www:~# apt-get
-y install php5 php5-cgi libapache2-mod-php5 php5-common php-pear
[2] Configure Apache2.
root@www:~# a2enconf php5-cgi.conf
Enabling conf php5-cgi.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
service apache2
reload
root@www:~# vi /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini
# line 879: uncomment and add
your timezone
date.timezone =
"Asia/Tokyo"
root@www:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting
web server apache2
...done.
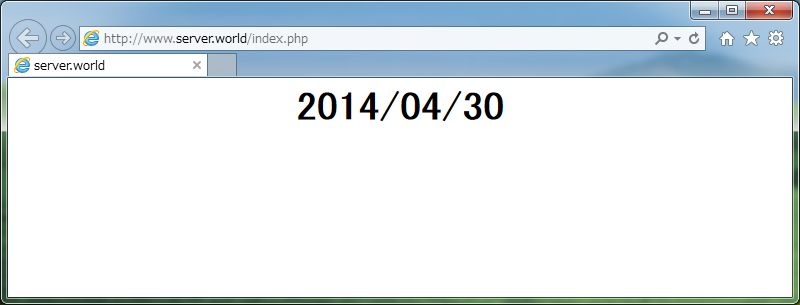
[3] Create a PHP test
page and access to it from any clients with web browser. It's OK if following
page is shown.
root@www:~# vi /var/www/html/index.php
<html>
<body>
<div style="width: 100%;
font-size: 40px; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;">
<?php
print Date("Y/m/d");
?>
</div>
</body>
</html>
C.
Nagios : Install
Install Nagios which is an enterprise open source monitoring system.
[1]Install and start Apache httpd, refer to here.
[1]Install and start Apache httpd, refer to here.
[2]Install PHP, refer to here.
[3] Install Nagios.
Also Install basic plugins to monitor nagios server itself.
root@dlp:~# apt-get -y install nagios3 nagios-plugins-basic
[4] Configure Nagios.
root@dlp:~# vi /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
# line 145: change
check_external_commands=1
root@dlp:~# vi /etc/nagios3/apache2.conf
# line 37: change access permission
Allow From localhost 10.0.0.0/24
# change admin password
root@dlp:~# htpasswd /etc/nagios3/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
New password: #
set password
Re-type new password:
Updating password for
user nagiosadmin
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/nagios3 restart
* Restarting nagios3
monitoring daemon nagios3
...done.
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
* Restarting web
server apache2
...done.
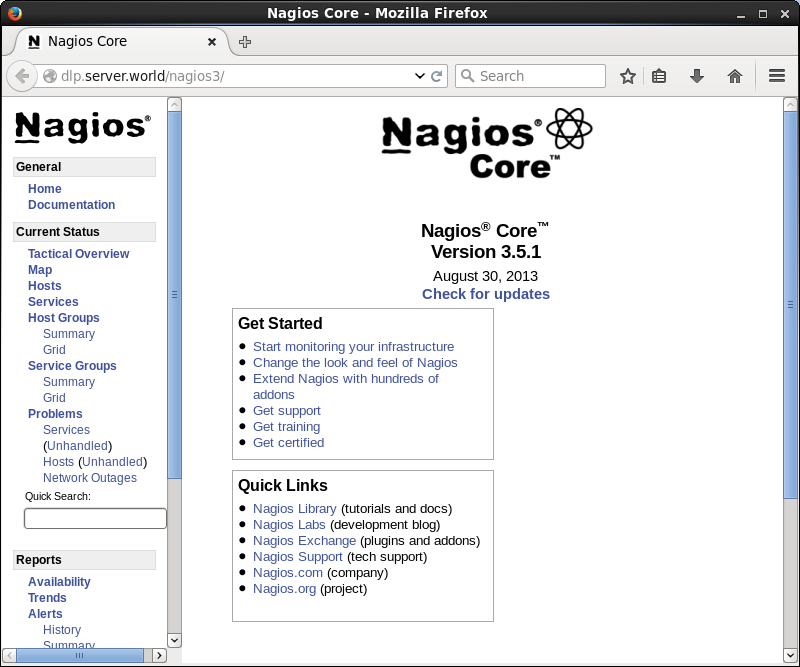
[5] Access to the
"http://(Nagios server's hostname or IP address)/nagios3/" from a
client which is in the network allowed by Nagios server and authenticate with
the Nagios admin user "nagiosadmin" to login.
[6] After successing
authentication, the Nagios admin site is displayed.
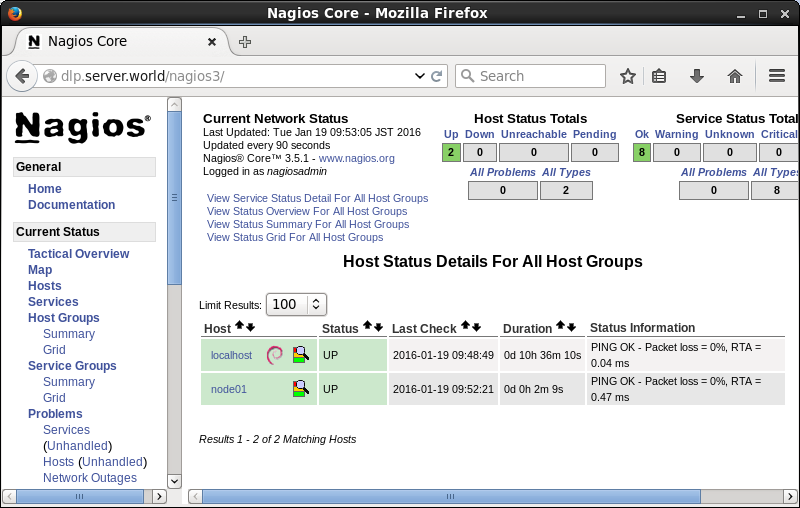
Nagios : Add Monitoring Target
Host#1
It's possible to monitor other servers on the network.
[1] For exmaple, add a
server for monitoring target with simply Ping command.
root@dlp:~# vi
/etc/nagios3/conf.d/node01.cfg
# create new
define host{
use generic-host
host_name node01
alias node01
address 10.0.0.51
}
use generic-service
host_name node01
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
}
root@dlp:~# /etc/init.d/nagios3 restart
[2] It's possible to view
the status for a new server on the admin site.